티스토리 뷰
이번 포스팅에서는 react-three/cannon을 활용하여 주사위 굴리기를 구현해보려고 합니다.
react-three/cannon란?
cannon-es을 기반으로 리액트에서 사용하기 쉽도록 만든 라이브러리로 물리적인 엔진을 적용하는데 사용하는 라이브러리입니다.
설치법
npm install @react-three/cannon
초기 세팅
Physics 컴포넌트로 물리적인 엔진을 적용할 컴포넌트를 감쌉니다.
App.jsx
<Canvas camera={{ position: [0, 50, 0], fov: 15 }} shadows>
<ambientLight intensity={0.5} />
<directionalLight position={[0, 100, 70]} intensity={1} castShadow />
<Physics gravity={[0, -30, 0]} defaultContactMaterial={{ restitution: 0.4 }}>
{/* Physics related objects in here please */}
</Physics>
<OrbitControls />
</Canvas>
- gravity : 중력을 적용할 수 있습니다. 지구의 중력은 [0, -9.81, 0] 입니다.
- restitution : 물체가 충돌 후 얼마나 튕겨나가지는지를 설정합니다.
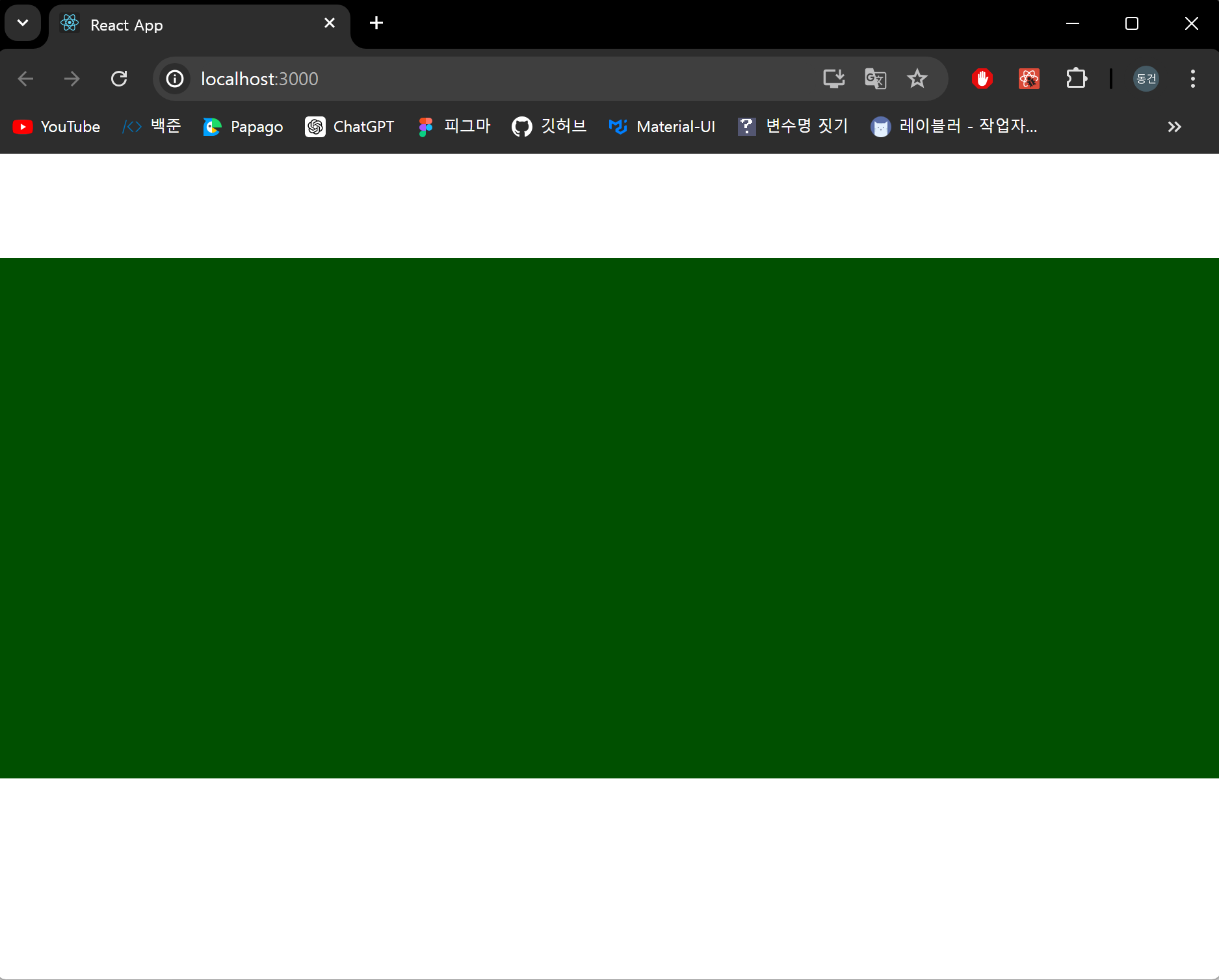
이제 땅을 생성해봅시다.
Ground.jsx
import { usePlane } from "@react-three/cannon";
export const Ground = () => {
const [ref] = usePlane(() => ({
rotation: [-Math.PI / 2, 0, 0],
position: [0, 0, 0],
}));
return (
<mesh ref={ref} receiveShadow>
<planeGeometry args={[100, 100]} />
<meshStandardMaterial color="green" />
</mesh>
);
};
usePlane : usePlane Hook을 통해 물리적 평면을 생성합니다.
rotatiton : 평면의 회전도를 설정합니다.
position : 평면의 위치를 지정합니다.
mesh 태그에 usePlane Hook에서 반환된 ref를 mesh에 연결하여 물리 엔진과 상호작용할 수 있도록 합니다.
만든 땅을 Physics 컴포넌트 사이에 넣습니다.
App.jsx
<Canvas camera={{ position: [0, 50, 0], fov: 15 }} shadows>
<ambientLight intensity={0.5} />
<directionalLight position={[0, 100, 70]} intensity={1} castShadow />
<Physics gravity={[0, -30, 0]} defaultContactMaterial={{ restitution: 0.4 }}>
<Ground />
</Physics>
<OrbitControls />
</Canvas>
결과 화면
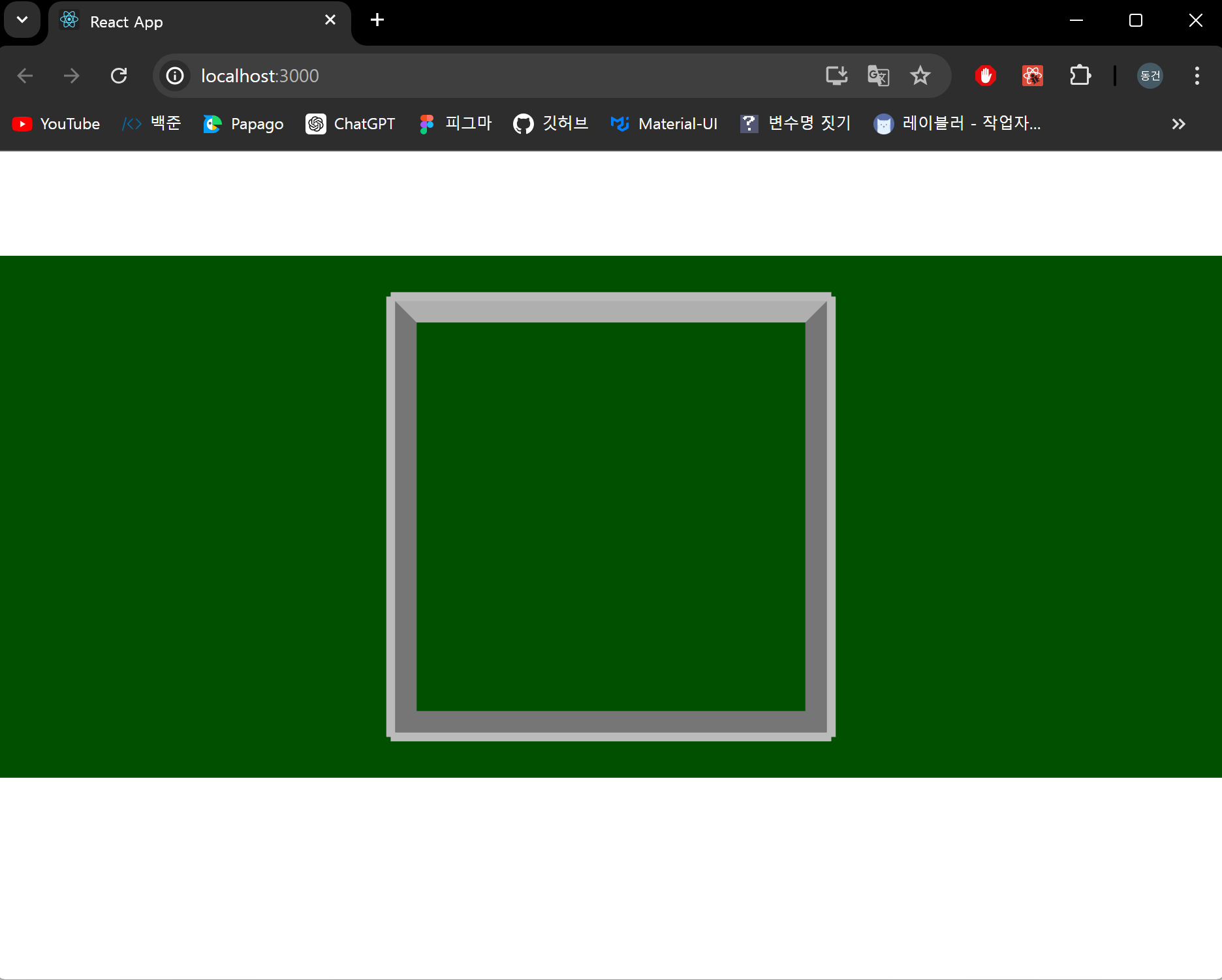
추가로 주사위를 굴릴때 너무 멀리 날아가지 않도록 벽을 생성해봅시다.
Wall.jsx
import { usePlane } from "@react-three/cannon";
export const Wall = ({ position, rotation, opacity }) => {
const [ref] = usePlane(() => ({
rotation: rotation,
position: position,
}));
return (
<mesh ref={ref}>
<boxGeometry args={[10, 5, 0.2]} />
<meshStandardMaterial transparent opacity={opacity} />
</mesh>
);
};
만든 벽을 Physics 컴포넌트 사이에 넣도록 합시다.
App.jsx
<Canvas camera={{ position: [0, 50, 0], fov: 15 }} shadows>
<ambientLight intensity={0.5} />
<directionalLight position={[0, 100, 70]} intensity={1} castShadow />
<Physics gravity={[0, -30, 0]} defaultContactMaterial={{ restitution: 0.4 }}>
<Ground />
<Wall position={[0, 2.5, -5]} rotation={[0, 0, 0]} opacity={100} />
<Wall position={[0, 2.5, 5]} rotation={[0, Math.PI, 0]} opacity={100} />
<Wall position={[-5, 2.5, 0]} rotation={[0, Math.PI / 2, 0]} opacity={100} />
<Wall position={[5, 2.5, 0]} rotation={[0, -Math.PI / 2, 0]} opacity={100} />
</Physics>
<OrbitControls />
</Canvas>
결과 화면
주사위를 던질 공간이 준비되었으니, 이제 주사위를 생성해봅시다.
Dice.jsx
import { useBox, useSphere } from "@react-three/cannon";
import { useGLTF } from "@react-three/drei";
import { useEffect, useMemo, useRef } from "react";
import * as THREE from "three";
export const Dice = ({ position }) => {
const { scene } = useGLTF("/dice/scene.gltf");
const copiedScene = useMemo(() => scene.clone(), [scene]);
const [ref, api] = useBox(() => ({
mass: 10,
position: position,
args: [1, 1, 1],
friction: 0.2,
restitution: 0.7,
}));
useEffect(() => {
if (copiedScene) {
copiedScene.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh) {
child.castShadow = true;
}
});
}
}, [copiedScene]);
return <primitive object={copiedScene} ref={ref} scale={[0.05, 0.05, 0.05]} />;
};
useGLTF : react-three/drei를 통해 gltf 형태인 주사위 3d 모델을 불러옵니다. 이때 불러온 모델은 자동적으로 캐싱이 되기 때문에 clone을 통해 모델을 복제하도록 합니다.
castShadow : 주사위에 그림자를 추가합니다.
api : 해당 물체의 물리적 속성을 조작할 수 있는 다양한 메서드를 포함하고 있습니다.
결과 화면
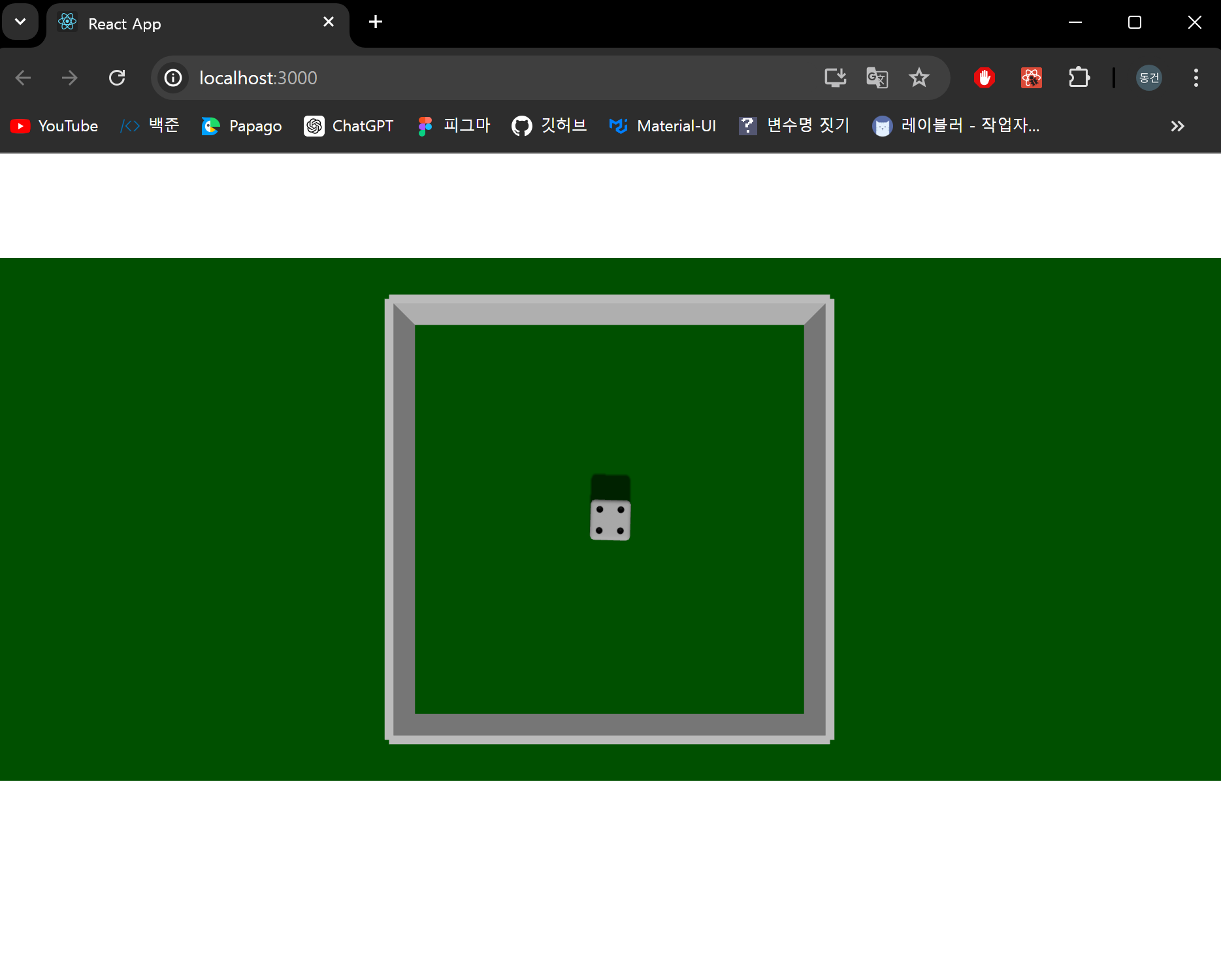
주사위가 정상적으로 생성됐습니다.
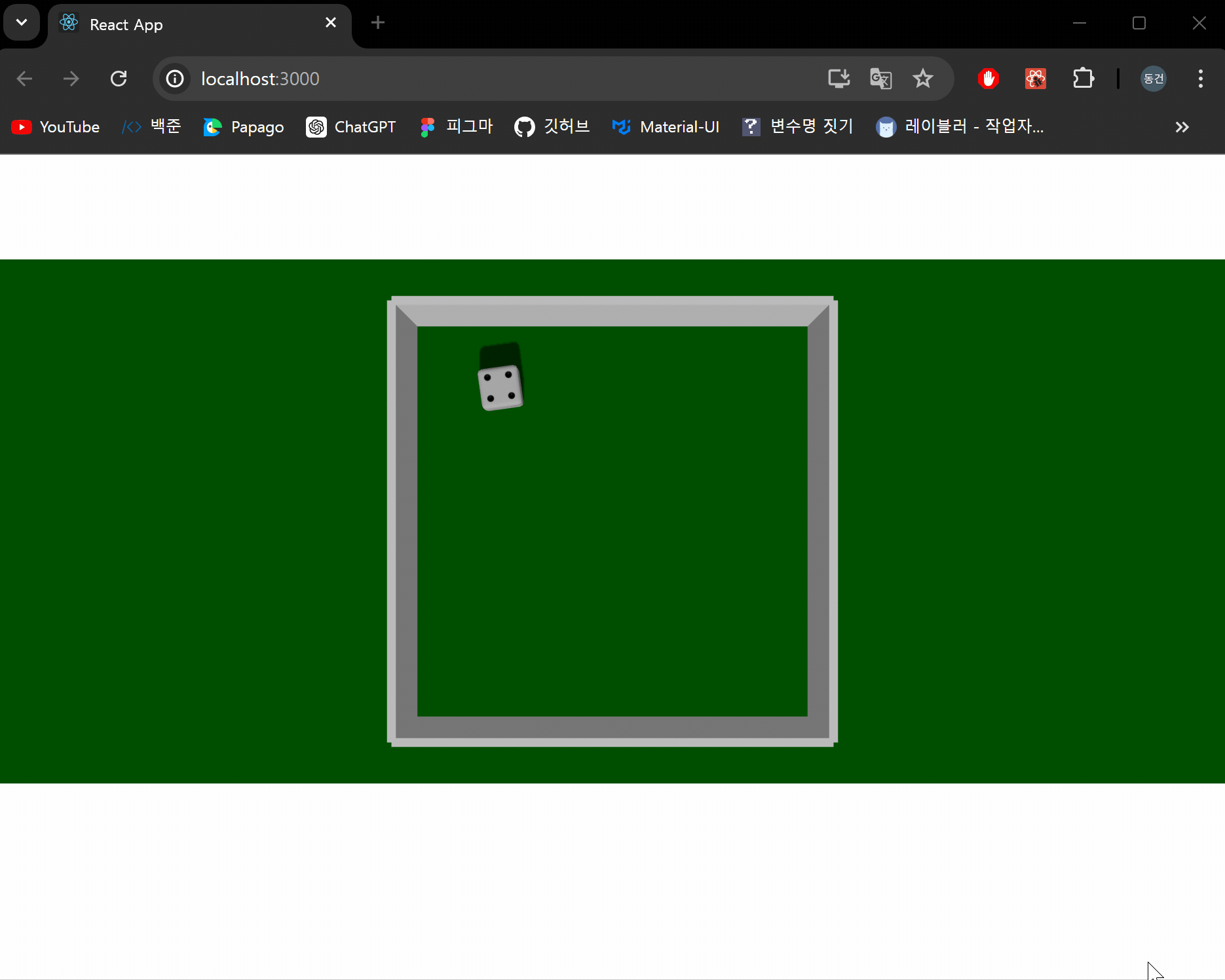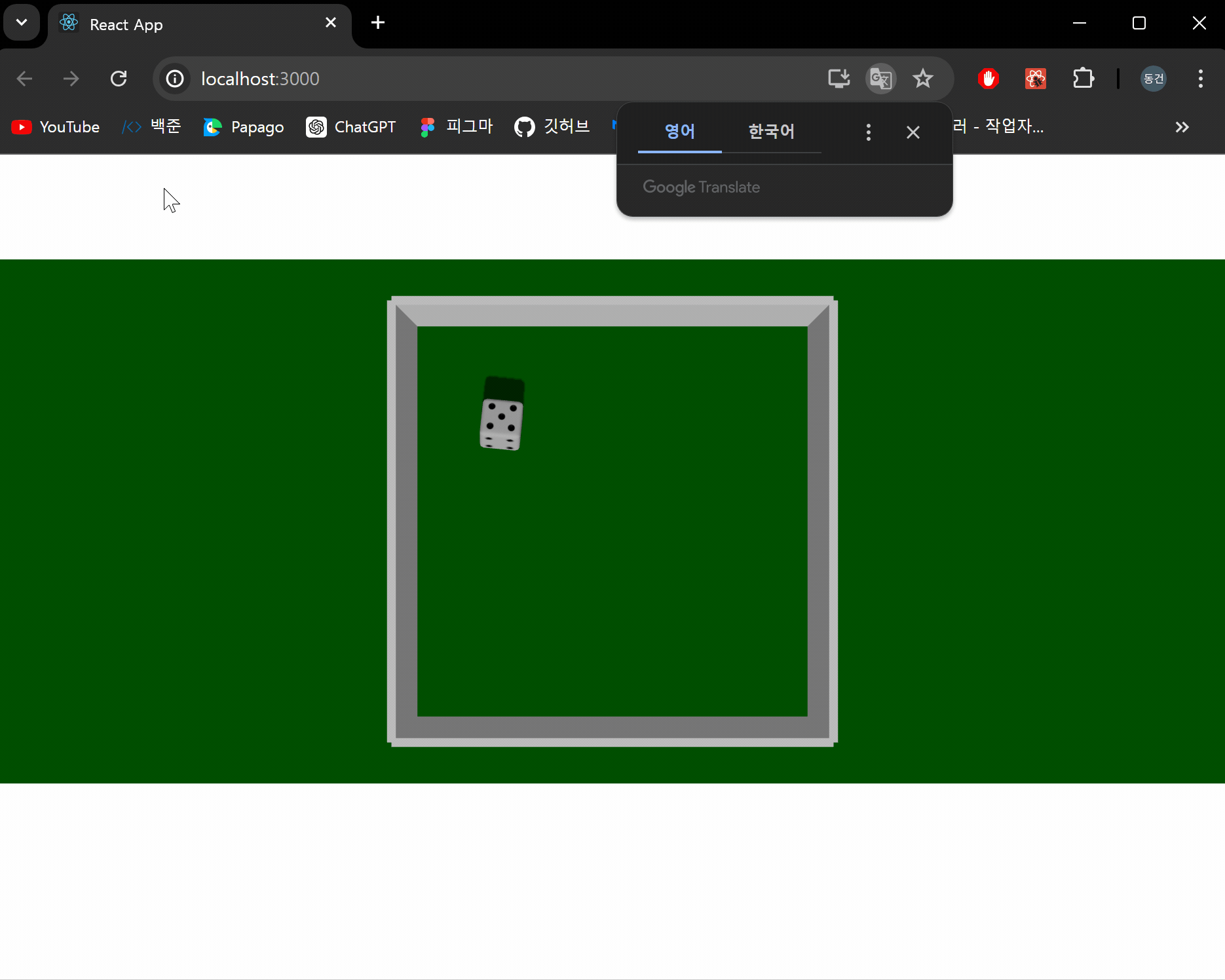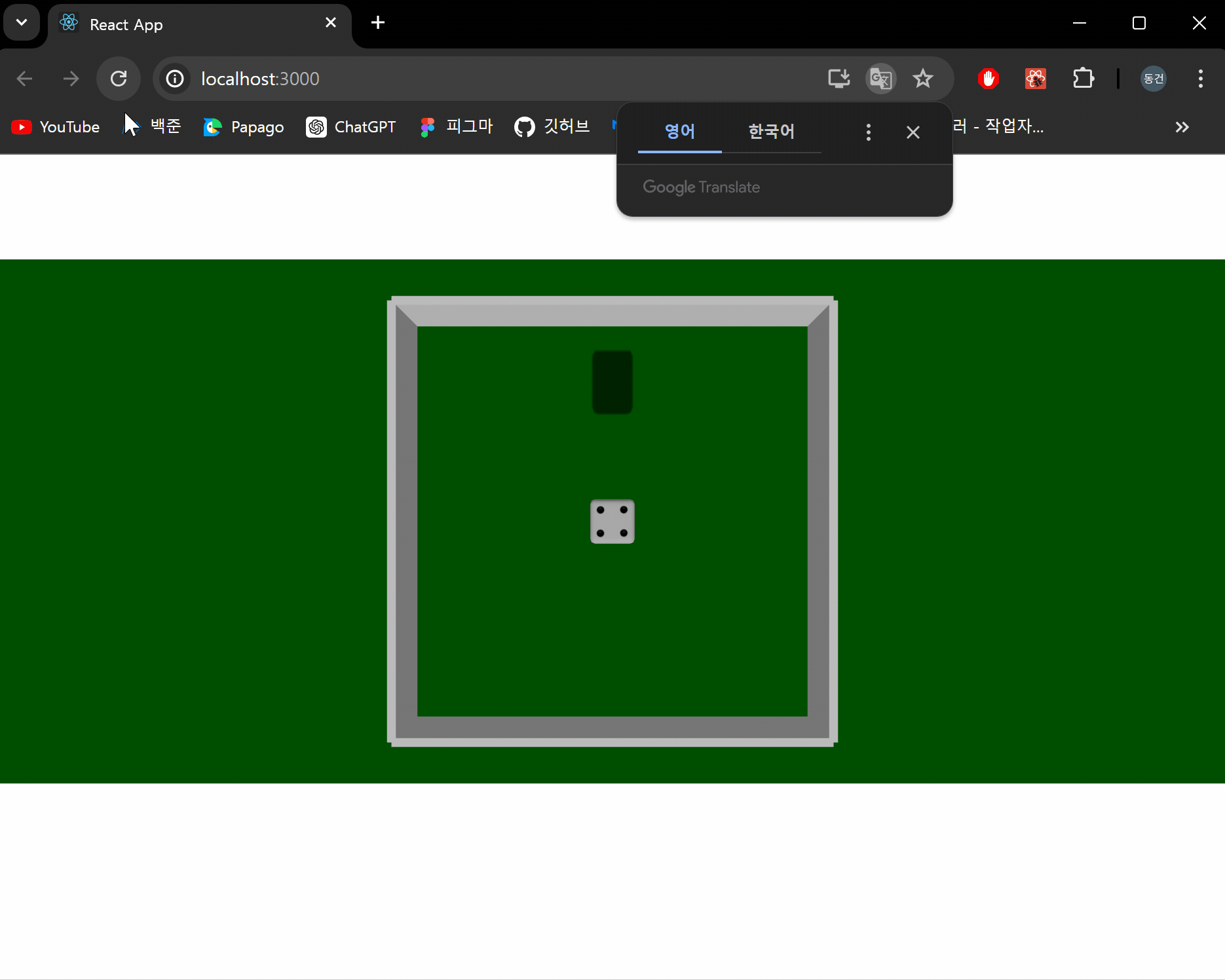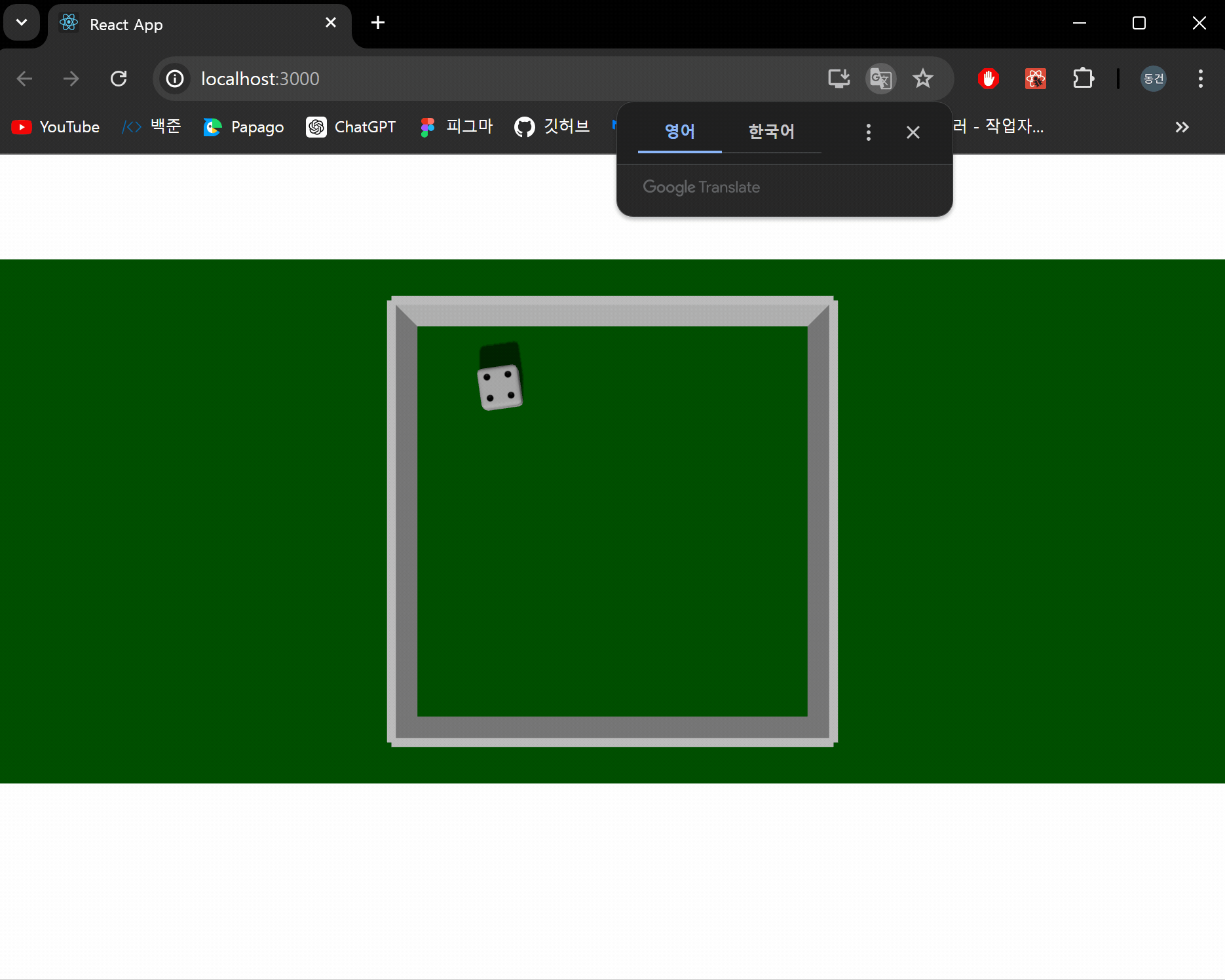
이제 주사위가 생성됐을때 충격을 주어 주사위가 회전하면서 떨어지도록 구현해보겠습니다.
Dice.jsx
import { useBox, useSphere } from "@react-three/cannon";
import { useGLTF } from "@react-three/drei";
import { useEffect, useMemo, useRef } from "react";
export const Dice = ({ gauge, position, setResults }) => {
const { scene } = useGLTF("/dice/scene.gltf");
const copiedScene = useMemo(() => scene.clone(), [scene]);
const [ref, api] = useBox(() => ({
mass: 10,
position: position,
args: [1, 1, 1],
friction: 0.2,
restitution: 0.7,
}));
useEffect(() => {
api.applyImpulse([-30, 10, 0], [0, 0.7, 0.3]);
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
if (copiedScene) {
copiedScene.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh) {
child.castShadow = true;
}
});
}
}, [copiedScene]);
return <primitive object={copiedScene} ref={ref} scale={[0.05, 0.05, 0.05]} />;
};
applyImpulse를 통해 충격을 줄 수 있습니다. 첫번째 인수는 물체에 가해지는 힘의 크기와 방향을 나타냅니다. 두번째 인수는 충격 지점으로, 이 지점에서 충격이 가해집니다. 이를 통해 물체의 회전도 조작할 수 있습니다.
결과 화면
이제 주사위 굴리기 버튼과 주사위 개수를 지정할 수 있는 인풋창을 생성해 사용자가 원하는 만큼 주사위를 굴릴 수 있도록 하도록 하겠습니다. 굴리기 버튼은 게이지를 통해 applyImpulse의 가해지는 힘을 설정할 수 있도록 구현하겠습니다.
App.jsx
function App() {
const [dices, setDices] = useState([]);
const [gauge, setGauge] = useState(0);
const [isPressing, setIsPressing] = useState(false);
const [numberOfDices, setNumberOfDices] = useState(2);
const reset = () => {
setDices([]);
};
const throwDice = () => {
setDices([]);
for (let i = 0; i < numberOfDices; i++) {
const position = [
Math.random() * 8 - 4, // -4 ~ 4 사이의 값
4,
Math.random() * 8 - 4, // -4 ~ 4 사이의 값
];
setDices((cube) => [
...cube,
<Dice key={cube.length} gauge={gauge} position={position} setResults={setResults} />,
]);
}
};
useEffect(() => {
let interval;
if (isPressing) {
interval = setInterval(() => {
setGauge((prev) => (prev < 100 ? prev + 1 : 0));
}, 10);
} else {
clearInterval(interval);
}
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, [isPressing]);
return (
<div style={{ marginTop: "80px", height: "400px" }}>
<input
type="number"
value={numberOfDices}
onChange={(e) => {
reset();
setNumberOfDices(parseInt(e.target.value));
}}
min="1"
max="10"
/>
<button
onMouseDown={() => setIsPressing(true)}
onMouseUp={() => {
setIsPressing(false);
throwDice();
setGauge(0);
}}
onTouchStart={() => setIsPressing(true)}
onTouchEnd={() => {
setIsPressing(false);
throwDice();
setGauge(0);
}}
>
주사위 굴리기
</button>
<button onClick={reset}>초기화</button>
<div>
<span>게이지: {gauge}</span>
</div>
</div>
);
}
isPressing 상태변수를 통해 버튼을 누르고 있는 상태를 판단하여 게이지를 1~100까지 채울 수 있도록 합니다.
throwDice 함수를 통해 지정한 주사위 개수만큼 dices 상태변수에 Dice 컴포넌트를 저장합니다. 이때 props로 넘겨지는 position은 벽 안쪽으로 생성되도록 하였습니다.
Dice 컴포넌트에 applyImpulse를 gauage 값으로 계산하도록 수정하도록 하겠습니다.
Dice.jsx
useEffect(() => {
const rad = Math.random() * Math.PI * 2;
const x = Math.cos(rad) * gauge;
const z = Math.sin(rad) * gauge;
api.applyImpulse([-x, 5, z], [0, 0.7, 0.3]);
}, []);
결과 화면
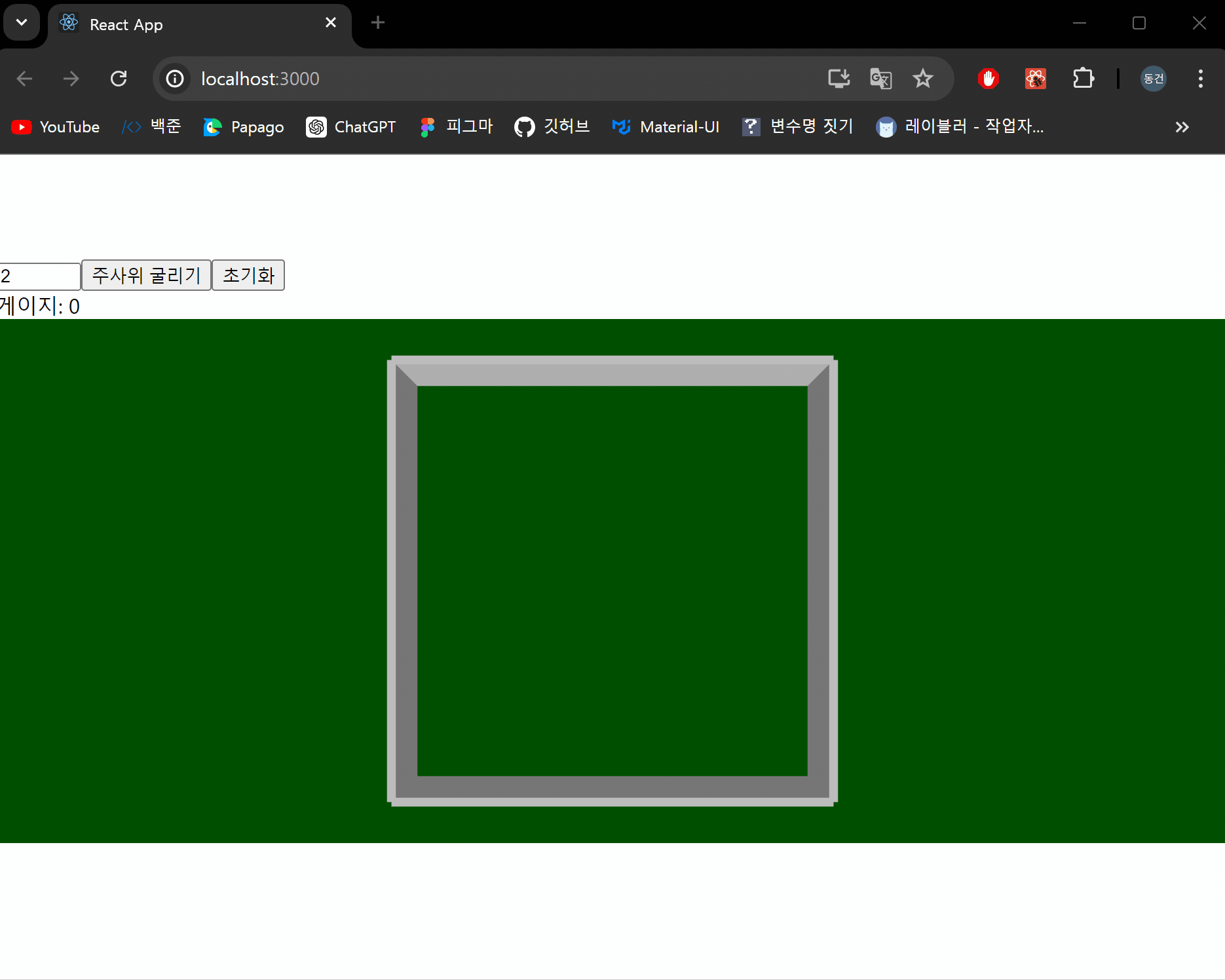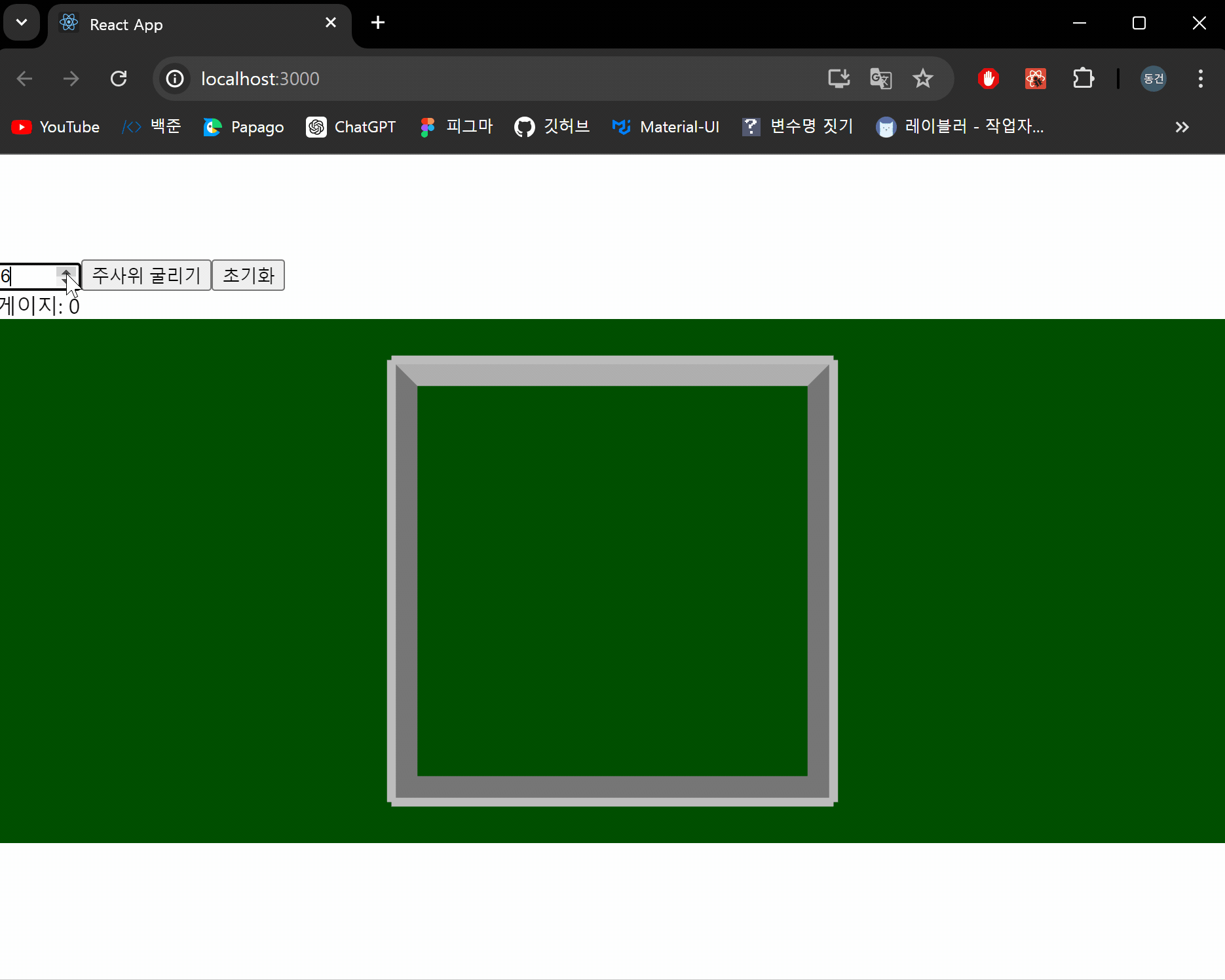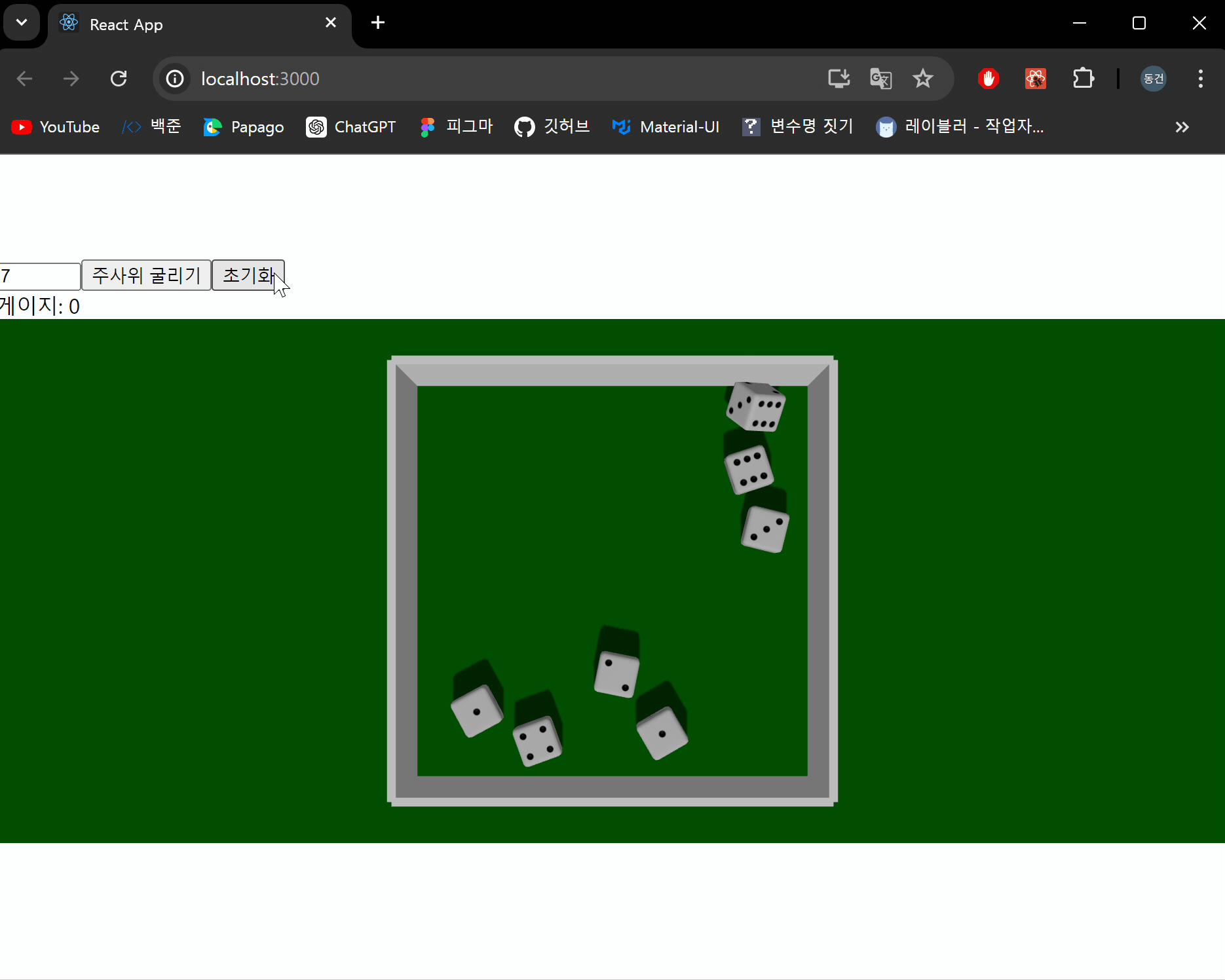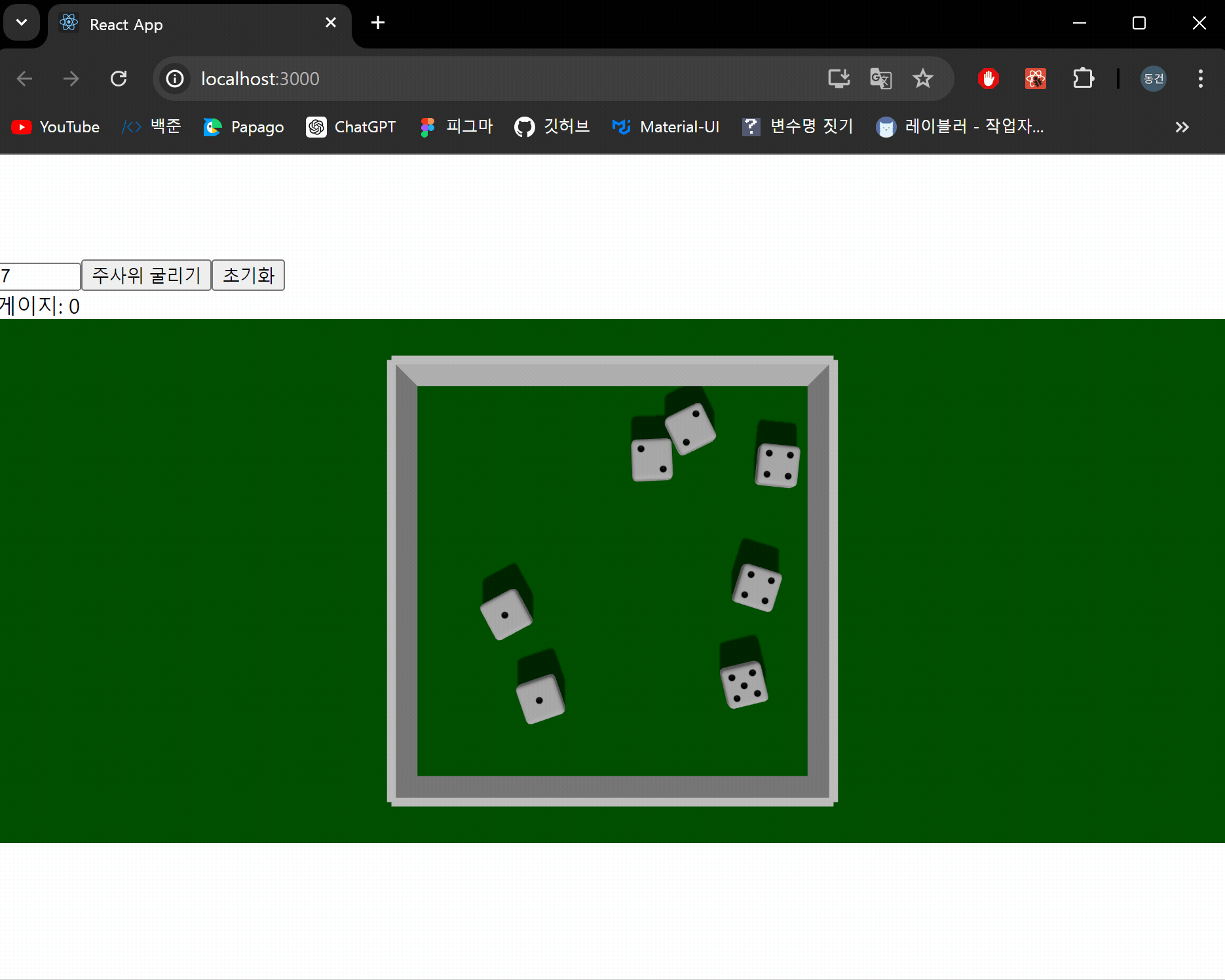
이제 주사위를 굴러 나온 눈금의 합계를 계산하는 기능을 구현하도록 하겠습니다.
주사위를 굴린 결과를 알아내기 위해 6면의 위치를 판단하여 계산합니다.
Dice.jsx
const calculateFacePositions = () => {
// 각 면의 위치를 저장할 배열 초기화
const facePositions = [];
// 각 면의 법선 벡터 정의
const faceNormals = [
new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1), // 앞면
new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, -1), // 뒷면
new THREE.Vector3(1, 0, 0), // 오른쪽 면
new THREE.Vector3(-1, 0, 0), // 왼쪽 면
new THREE.Vector3(0, 1, 0), // 윗면
new THREE.Vector3(0, -1, 0), // 아랫면
];
// 객체의 현재 회전을 나타내는 쿼터니언 가져오기
const quaternion = new THREE.Quaternion();
ref.current.getWorldQuaternion(quaternion);
// 각 법선 벡터에 대해 반복하여 면의 위치 계산
faceNormals.forEach((normal) => {
// 법선 벡터를 회전시킴
const rotatedNormal = normal.clone().applyQuaternion(quaternion);
// 객체의 위치에 회전된 법선 벡터를 더하여 면의 위치 계산
const facePosition = new THREE.Vector3().copy(ref.current.position).add(rotatedNormal);
// 계산된 면의 위치를 배열에 추가
facePositions.push(facePosition);
});
// 면의 위치 배열 반환
return facePositions;
};
법선 벡터를 정의하고, 객체의 회전을 고려하여 회전된 법선 벡터를 계산한 후, 객체의 현재 위치와 결합하여 각 면의 위치를 구합니다. 이 계산을 통해 객체가 회전한 상태에서도 각 면의 위치를 정확히 파악할 수 있습니다.
주사위가 구르고 난 후에 멈춰있을 때 눈금을 계산해야하기 때문에 velocity 값이 0.01 이하일 때 눈금을 계산하도록 합니다.
Dice.jsx
useEffect(() => {
const unsubscribeVelocity = api.velocity.subscribe((v) => {
if (v.every((value) => Math.abs(value) < 0.01)) {
calculateFacePositions();
unsubscribeVelocity(); // Unsubscribe to prevent the loop
}
});
}, [api]);
주사위를 굴러서 멈췄을 때에 계산 값들을 보면 눈금마다 각 면의 y축 높이가 다른 것을 알 수 있습니다.
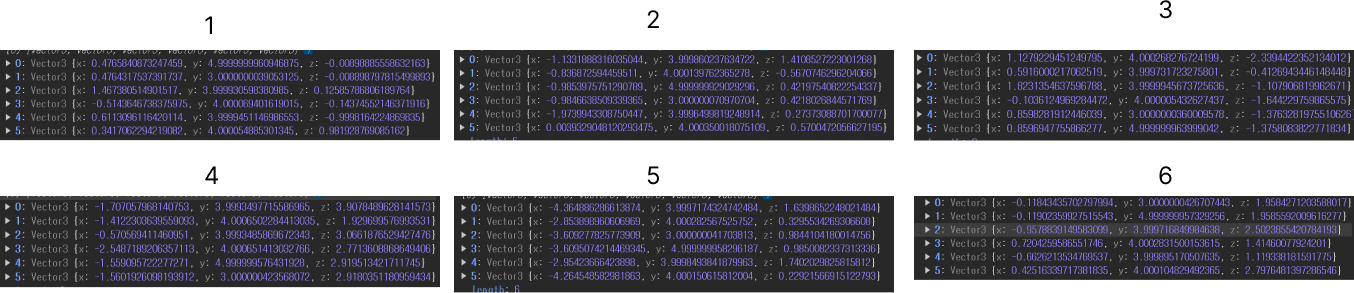
이 값들을 통해 6면 중에 가장 높은 면의 인덱스에 따라 눈금을 판단할 수 있습니다.
Dice.jsx
const diceScale = {
0: 1,
1: 6,
2: 2,
3: 5,
4: 4,
5: 3,
};
const facePositions = calculateFacePositions();
let maxY = -Infinity;
let maxIndex = -1;
facePositions.forEach((item, index) => {
if (item.y > maxY) {
maxY = item.y;
maxIndex = index;
}
});
console.log("눈금:", diceScale[maxIndex]);
이 값을 상태 변수에 저장하여 눈금 결과와 눈금의 모든 수를 더해 보여주도록 합시다.
Dice.jsx
const handleSleep = () => {
const diceScale = {
0: 1,
1: 6,
2: 2,
3: 5,
4: 4,
5: 3,
};
const facePositions = calculateFacePositions();
let maxY = -Infinity;
let maxIndex = -1;
facePositions.forEach((item, index) => {
if (item.y > maxY) {
maxY = item.y;
maxIndex = index;
}
});
setResults((result) => [...result, diceScale[maxIndex]]);
console.log("눈금:", diceScale[maxIndex]);
};
useEffect(() => {
const unsubscribeVelocity = api.velocity.subscribe((v) => {
if (v.every((value) => Math.abs(value) < 0.01)) {
handleSleep();
unsubscribeVelocity(); // Unsubscribe to prevent the loop
}
});
}, [api]);
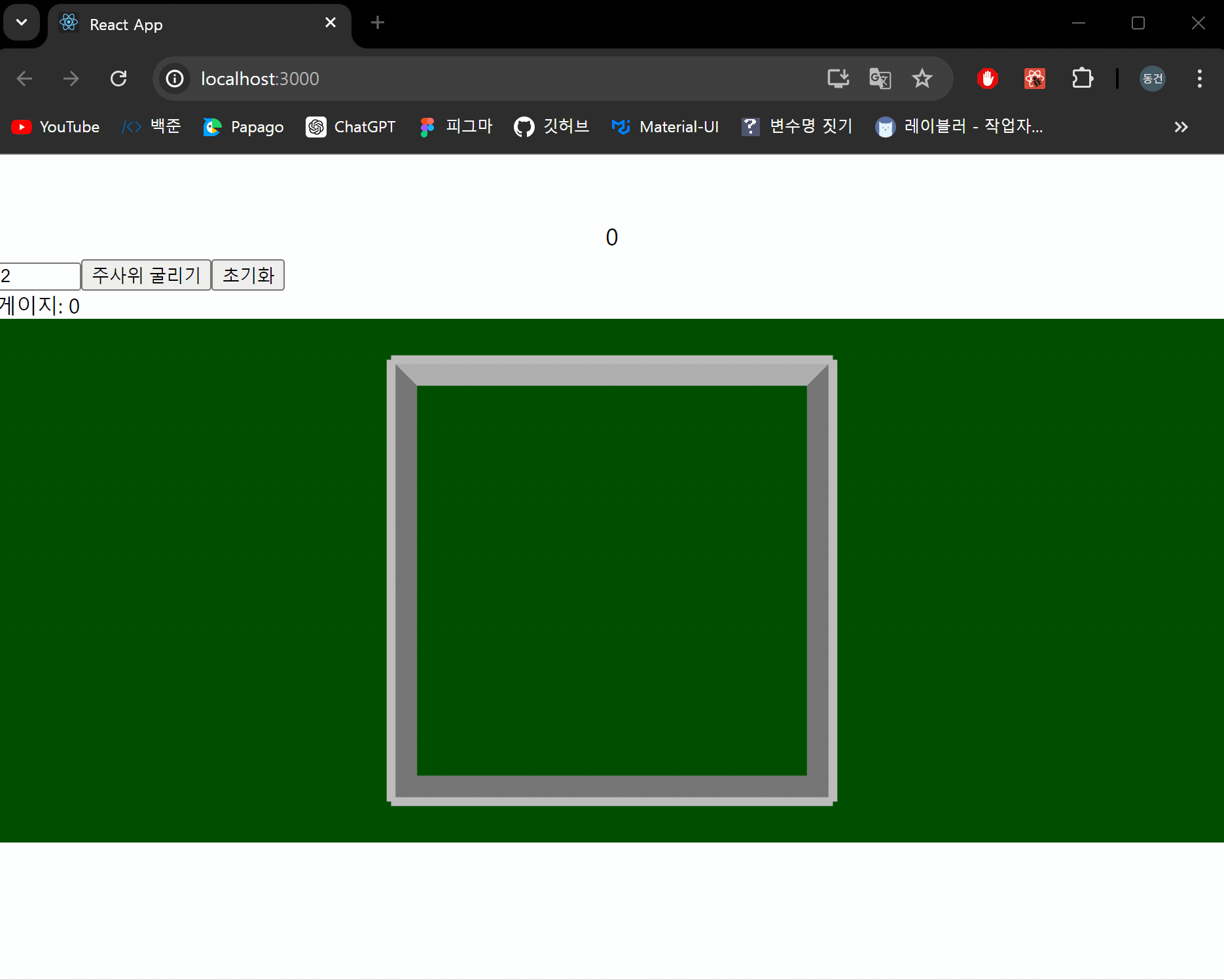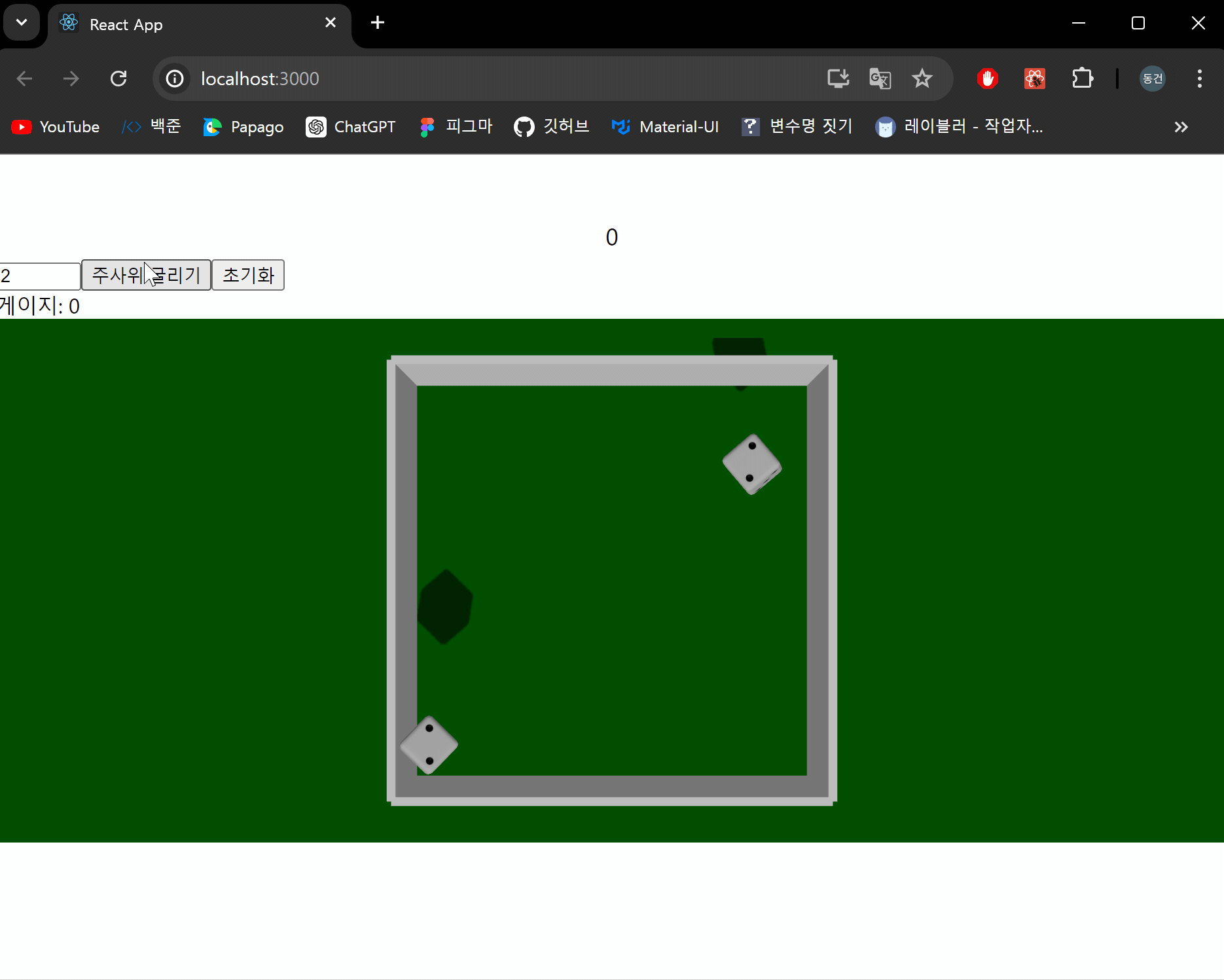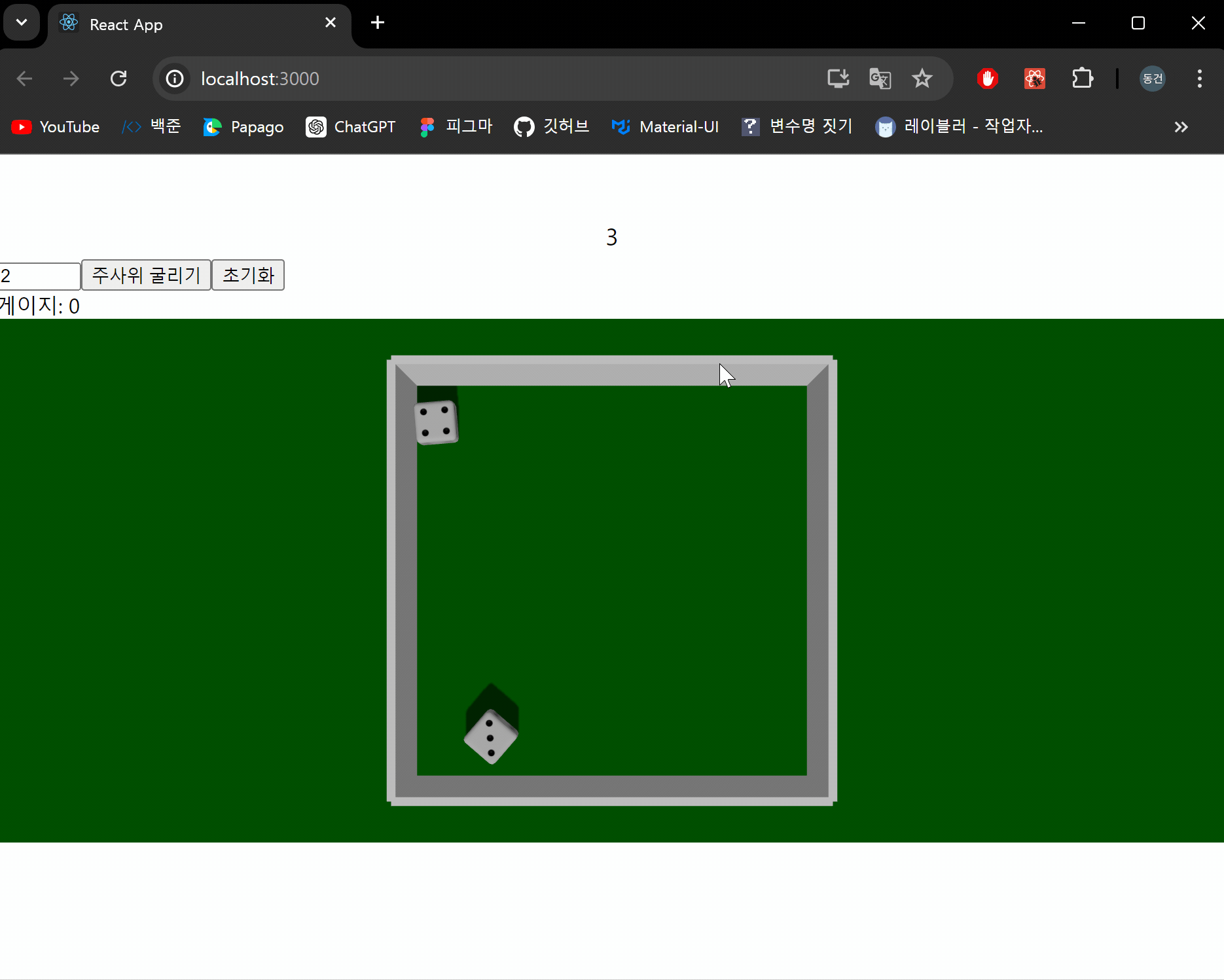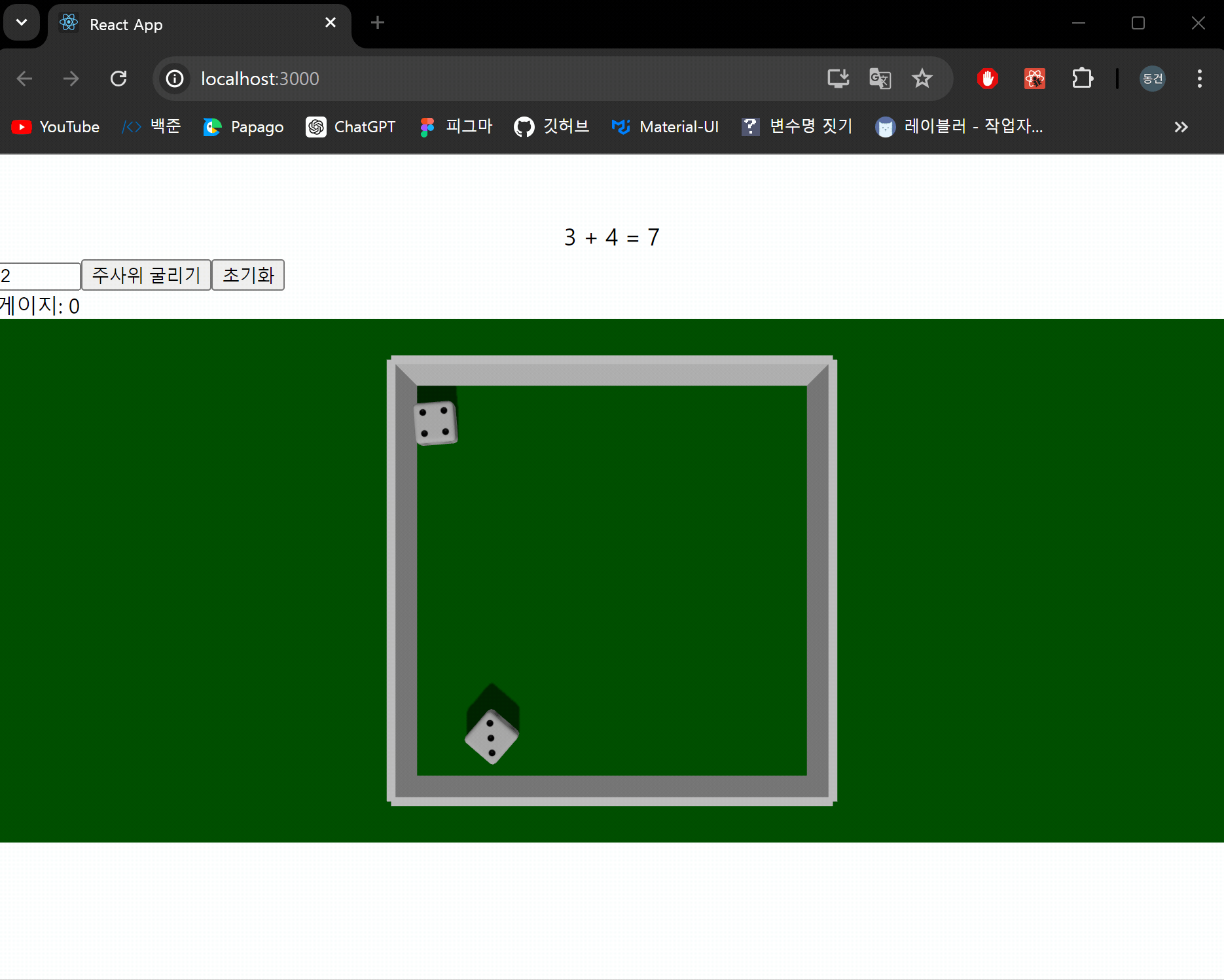
저장된 값을 통해 화면에 보여주도록 하고 합계도 보여주도록 하겠습니다.
App.jsx
const formattedResults = results.reduce((acc, result, index) => {
if (index === results.length - 1) {
return acc + result + " = ";
} else {
return acc + result + " + ";
}
}, "");
// 결과 값의 합계 계산
const sum = results.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0);
<span>
{results.length > 1 && formattedResults}
{sum}
</span>
결과 화면
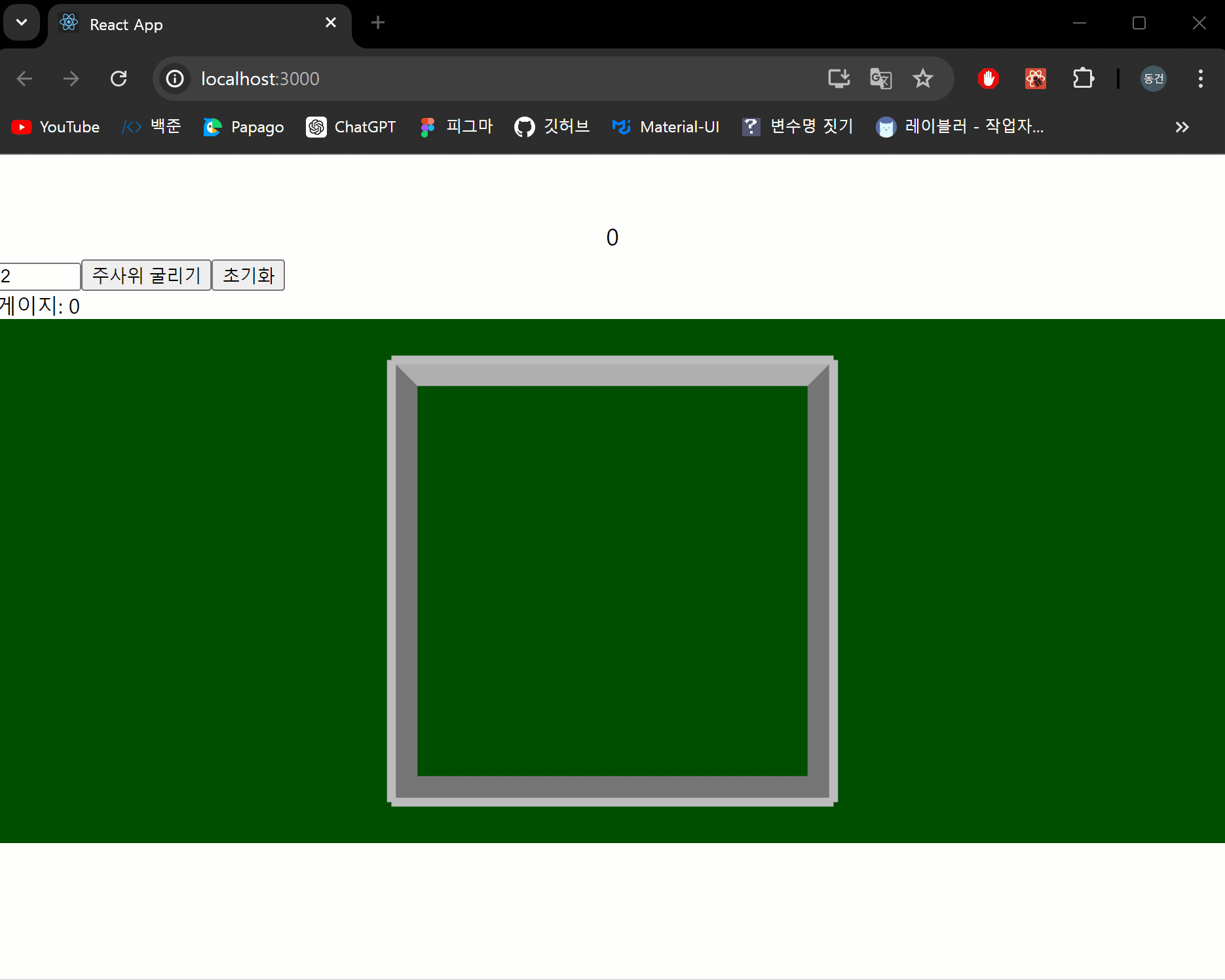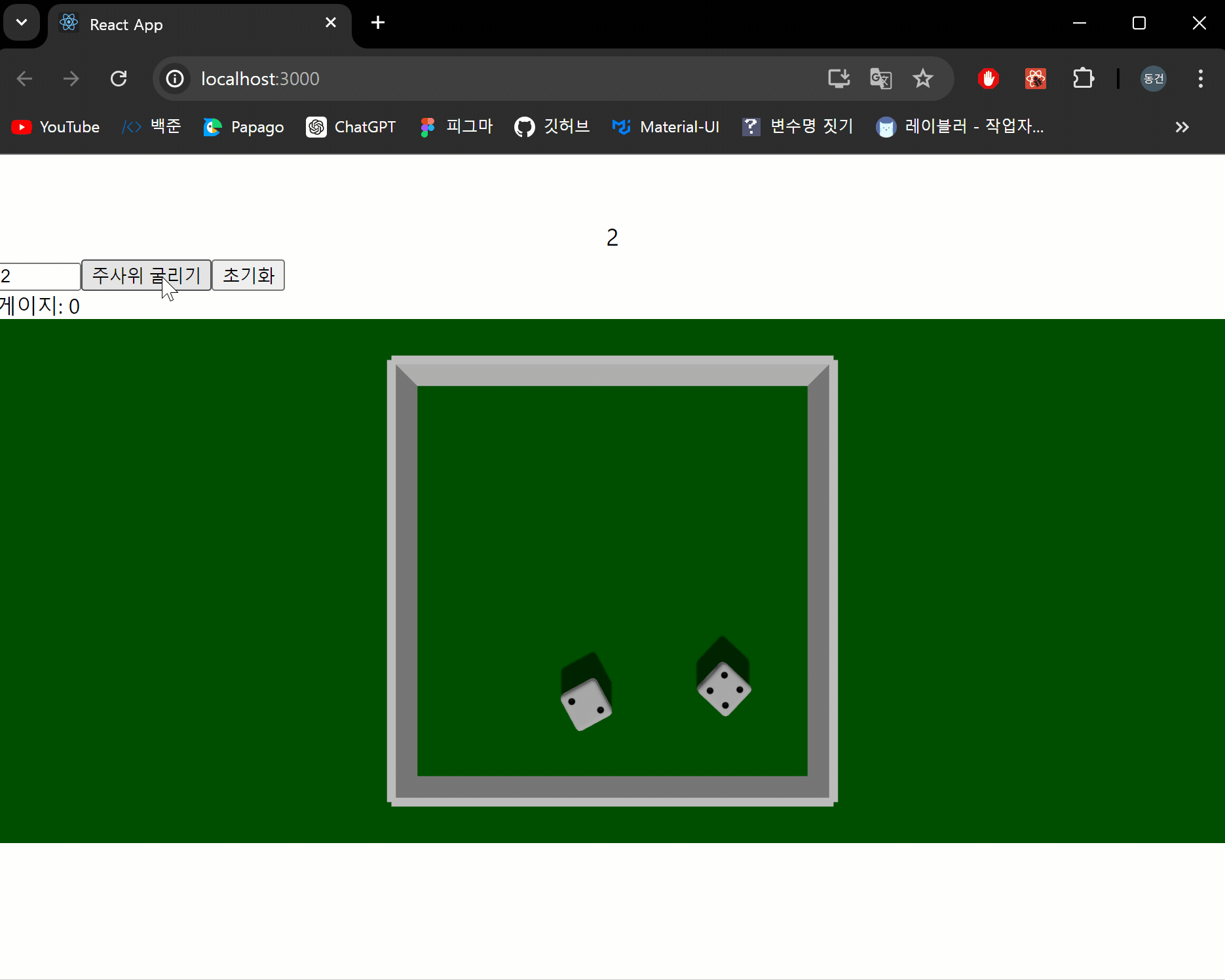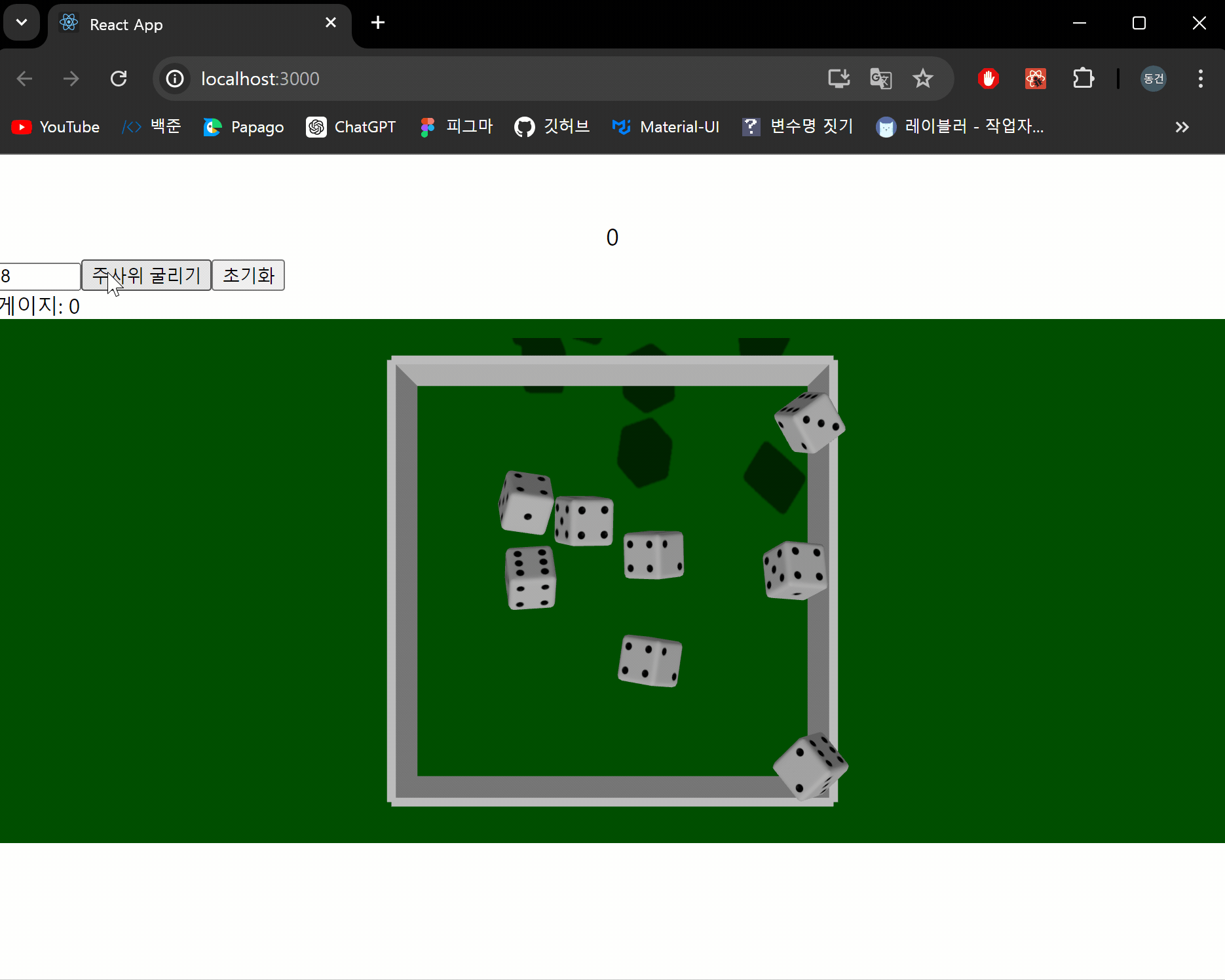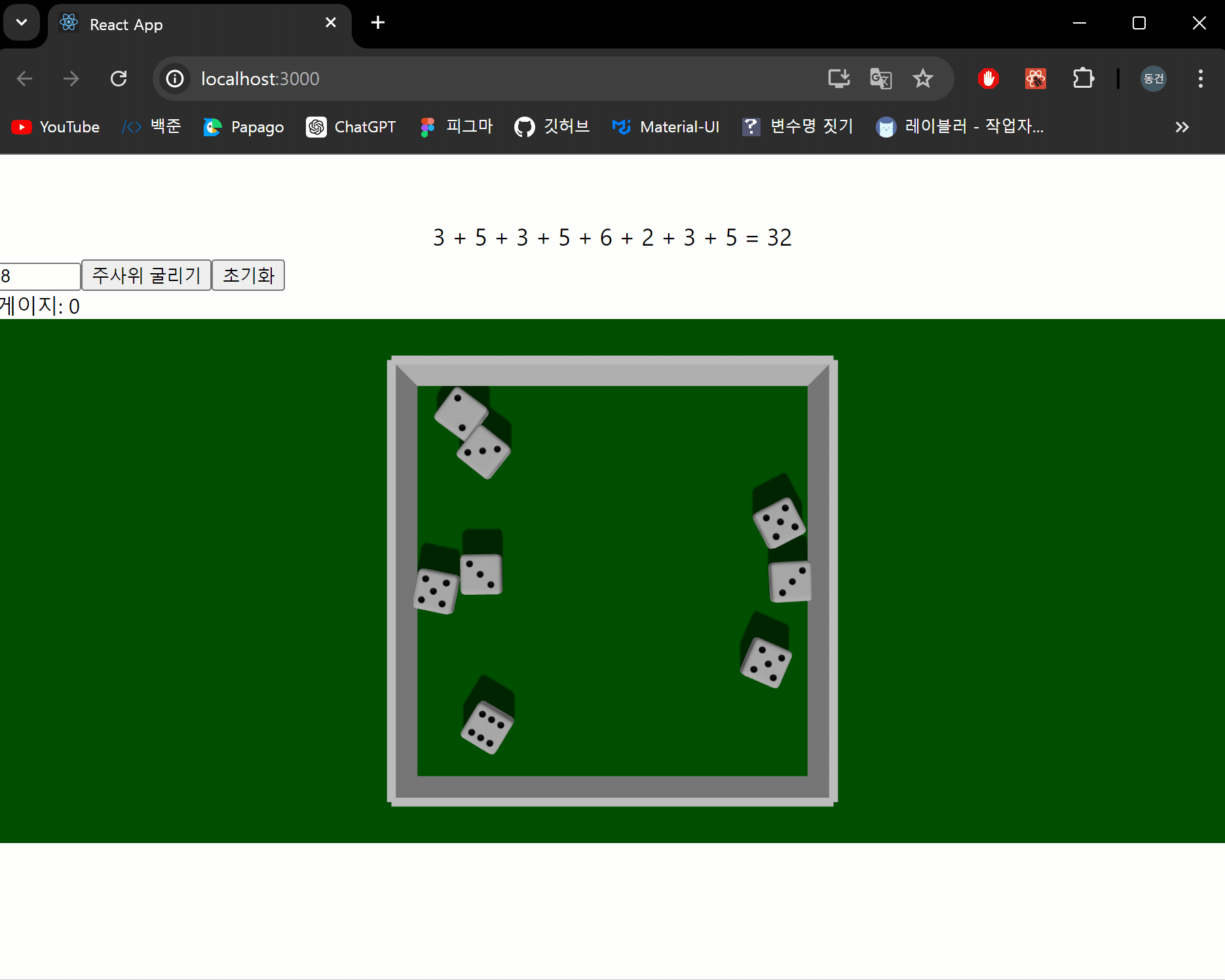
잘 작동하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다!
전체 코드
App.jsx
import { Canvas } from "@react-three/fiber";
import { OrbitControls, Text } from "@react-three/drei";
import { Physics } from "@react-three/cannon";
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { Ground } from "./components/Ground";
import { Wall } from "./components/Wall";
import { Dice } from "./components/Dice";
function App() {
const [dices, setDices] = useState([]);
const [gauge, setGauge] = useState(0);
const [isPressing, setIsPressing] = useState(false);
const [numberOfDices, setNumberOfDices] = useState(2);
const [results, setResults] = useState([]);
const reset = () => {
setResults([]);
setDices([]);
};
const throwDice = () => {
setDices([]);
for (let i = 0; i < numberOfDices; i++) {
const position = [
Math.random() * 8 - 4, // -4 ~ 4 사이의 값
Math.random() * 4 + 5,
Math.random() * 8 - 4, // -4 ~ 4 사이의 값
];
setDices((cube) => [
...cube,
<Dice key={cube.length} gauge={gauge} position={position} setResults={setResults} />,
]);
}
};
useEffect(() => {
let interval;
if (isPressing) {
interval = setInterval(() => {
setGauge((prev) => (prev < 100 ? prev + 1 : 0));
}, 10);
} else {
clearInterval(interval);
}
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, [isPressing]);
const formattedResults = results.reduce((acc, result, index) => {
if (index === results.length - 1) {
return acc + result + " = ";
} else {
return acc + result + " + ";
}
}, "");
// 결과 값의 합계 계산
const sum = results.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0);
return (
<div style={{ marginTop: "80px", height: "400px" }}>
<div
style={{
position: "absolute",
width: "100%",
display: "flex",
justifyContent: "center",
zIndex: "-999",
top: "50px",
fontSize: "18px",
}}
>
<span>
{results.length > 1 && formattedResults}
{sum}
</span>
</div>
<input
type="number"
value={numberOfDices}
onChange={(e) => {
reset();
setNumberOfDices(parseInt(e.target.value));
}}
min="1"
max="10"
/>
<button
onMouseDown={() => setIsPressing(true)}
onMouseUp={() => {
setIsPressing(false);
throwDice();
setGauge(0);
}}
onTouchStart={() => setIsPressing(true)}
onTouchEnd={() => {
setIsPressing(false);
throwDice();
setGauge(0);
}}
>
주사위 굴리기
</button>
<button onClick={reset}>초기화</button>
<div>
<span>게이지: {gauge}</span>
</div>
<Canvas camera={{ position: [0, 50, 0], fov: 15 }} shadows>
<ambientLight intensity={0.5} />
<directionalLight position={[0, 100, 70]} intensity={1} castShadow />
<Physics gravity={[0, -30, 0]} defaultContactMaterial={{ restitution: 0.3 }}>
<Ground />
<Wall position={[0, 2.5, -5]} rotation={[0, 0, 0]} opacity={100} />
<Wall position={[0, 2.5, 5]} rotation={[0, Math.PI, 0]} opacity={100} />
<Wall position={[-5, 2.5, 0]} rotation={[0, Math.PI / 2, 0]} opacity={100} />
<Wall position={[5, 2.5, 0]} rotation={[0, -Math.PI / 2, 0]} opacity={100} />
{dices.map((dice) => dice)}
</Physics>
<OrbitControls />
</Canvas>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Dice.jsx
import { useBox, useSphere } from "@react-three/cannon";
import { useGLTF } from "@react-three/drei";
import { useEffect, useMemo, useRef } from "react";
import * as THREE from "three";
export const Dice = ({ gauge, position, setResults }) => {
const { scene } = useGLTF("/dice/scene.gltf");
const copiedScene = useMemo(() => scene.clone(), [scene]);
const [ref, api] = useBox(() => ({
mass: 10,
position: position,
args: [1, 1, 1],
friction: 0.2,
restitution: 0.7,
}));
useEffect(() => {
const rad = Math.random() * Math.PI * 2;
const x = Math.cos(rad) * gauge;
const z = Math.sin(rad) * gauge;
api.applyImpulse([-x, 5, z], [0, 0.7, 0.3]);
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
if (copiedScene) {
copiedScene.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh) {
child.castShadow = true;
}
});
}
}, [copiedScene]);
const calculateFacePositions = () => {
// 각 면의 위치를 저장할 배열 초기화
const facePositions = [];
// 각 면의 법선 벡터 정의
const faceNormals = [
new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1), // 앞면
new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, -1), // 뒷면
new THREE.Vector3(1, 0, 0), // 오른쪽 면
new THREE.Vector3(-1, 0, 0), // 왼쪽 면
new THREE.Vector3(0, 1, 0), // 윗면
new THREE.Vector3(0, -1, 0), // 아랫면
];
// 객체의 현재 회전을 나타내는 쿼터니언 가져오기
const quaternion = new THREE.Quaternion();
ref.current.getWorldQuaternion(quaternion);
// 각 법선 벡터에 대해 반복하여 면의 위치 계산
faceNormals.forEach((normal) => {
// 법선 벡터를 회전시킴
const rotatedNormal = normal.clone().applyQuaternion(quaternion);
// 객체의 위치에 회전된 법선 벡터를 더하여 면의 위치 계산
const facePosition = new THREE.Vector3().copy(ref.current.position).add(rotatedNormal);
// 계산된 면의 위치를 배열에 추가
facePositions.push(facePosition);
});
// 면의 위치 배열 반환
return facePositions;
};
const handleSleep = () => {
const diceScale = {
0: 1,
1: 6,
2: 2,
3: 5,
4: 4,
5: 3,
};
const facePositions = calculateFacePositions();
let maxY = -Infinity;
let maxIndex = -1;
facePositions.forEach((item, index) => {
if (item.y > maxY) {
maxY = item.y;
maxIndex = index;
}
});
setResults((result) => [...result, diceScale[maxIndex]]);
console.log("눈금:", diceScale[maxIndex]);
};
useEffect(() => {
const unsubscribeVelocity = api.velocity.subscribe((v) => {
if (v.every((value) => Math.abs(value) < 0.01)) {
handleSleep();
unsubscribeVelocity(); // Unsubscribe to prevent the loop
}
});
}, [api]);
return <primitive object={copiedScene} ref={ref} scale={[0.05, 0.05, 0.05]} />;
};
이상으로 리액트에서 cannon을 통해 주사위 굴리는 방법에 대해 알아보았습니다. 물리적인 요소가 많이 들어가 있어 어려운 부분이 있었지만 구글링을 통해 어찌저찌 잘 구현해 볼 수 있었습니다. 게임 만드시는 분들이 얼마나 많은 노고를 통해 만들었는지 느끼게 되었습니다.
참고
https://github.com/pmndrs/use-cannon/tree/master
GitHub - pmndrs/use-cannon: 👋💣 physics based hooks for @react-three/fiber
👋💣 physics based hooks for @react-three/fiber. Contribute to pmndrs/use-cannon development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
https://pmndrs.github.io/cannon-es/docs/classes/Body.html#applyForce
Body | cannon-es
The self object, for chainability.
pmndrs.github.io
'React.js' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [React.js] Raect-three-fiber 알아보기 (0) | 2024.07.14 |
|---|---|
| [React.js] React와 EventEmitter3를 활용하여 STOMP WebSocket 메시지 처리하기 (0) | 2024.06.04 |
| [React.js] React.js에서의 클로저(컴포넌트 상태 관리의 이해) (0) | 2024.05.21 |
| [React.js] 메모리제이션을 통해 성능 최적화 하기 (0) | 2024.05.20 |
| [React.js] axios.interceptors를 이용하여 액세스 토큰 재발급 및 헤더 설정하기 (0) | 2024.05.15 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 9575
- react-three-fiber
- 4659
- 24431
- useCallback
- useMemo
- 20551
- react.memo
- Next.js
- RefreshToken
- eventemitter3
- rc-dock
- revalidateTag
- web3
- NextAuth
- baekjoon
- js
- stompjs
- revalidatePath
- dynamic routing
- React
- 해시를 사용한 집합과 맵
- 25329
- useState
- react-query
- useQuery
- sepolia
- 백준
- React.JS
- zustand
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
